PDF] Acute ankle sprain in athletes: Clinical aspects and
4.8 (741) In stock

Excessive imaging, unwarranted non-weight-bearing, unjustified immobilization, delay in functional movements, and inadequate rehabilitation are common myths and mistakes in the management of ankle sprains. Acute ankle sprain is the most common lower limb injury in athletes and accounts for 16%-40% of all sports-related injuries. It is especially common in basketball, American football, and soccer. The majority of sprains affect the lateral ligaments, particularly the anterior talofibular ligament. Despite its high prevalence, a high proportion of patients experience persistent residual symptoms and injury recurrence. A detailed history and proper physical examination are diagnostic cornerstones. Imaging is not indicated for the majority of ankle sprain cases and should be requested according to the Ottawa ankle rules. Several interventions have been recommended in the management of acute ankle sprains including rest, ice, compression, and elevation, analgesic and anti-inflammatory medications, bracing and immobilization, early weight-bearing and walking aids, foot orthoses, manual therapy, exercise therapy, electrophysical modalities and surgery (only in selected refractory cases). Among these interventions, exercise and bracing have been recommended with a higher level of evidence and should be incorporated in the rehabilitation process. An exercise program should be comprehensive and progressive including the range of motion, stretching, strengthening, neuromuscular, proprioceptive, and sport-specific exercises. Decision-making regarding return to the sport in athletes may be challenging and a sports physician should determine this based on the self-reported variables, manual tests for stability, and functional performance testing. There are some common myths and mistakes in the management of ankle sprains, which all clinicians should be aware of and avoid. These include excessive imaging, unwarranted non-weight-bearing, unjustified immobilization, delay in functional movements, and inadequate rehabilitation. The application of an evidence-based algorithmic approach considering the individual characteristics is helpful and should be recommended.
media.springer/full/springer-static/imag

PDF) Ankle sprain: Diagnosis and therapy starts with knowledge of

Risk factors for chronic ankle instability after first episode of
Frontiers Acute Effect of Kinesiology Taping on Postural

The epidemiology, evaluation, and assessment of lateral ankle

The epidemiology, evaluation, and assessment of lateral ankle

PDF) Acute ankle sprain in athletes: Clinical aspects and

Quick and simple test to evaluate severity of acute lateral ankle

Frontiers Differences in health-related quality of life among

Understanding acute ankle ligamentous sprain injury in sports

Most ankle sprain research is either false or clinically

Early Ankle Sprain Rehab And Exercises - Foot/ankle

PDF) Treatment and prevention of acute and recurrent ankle sprain
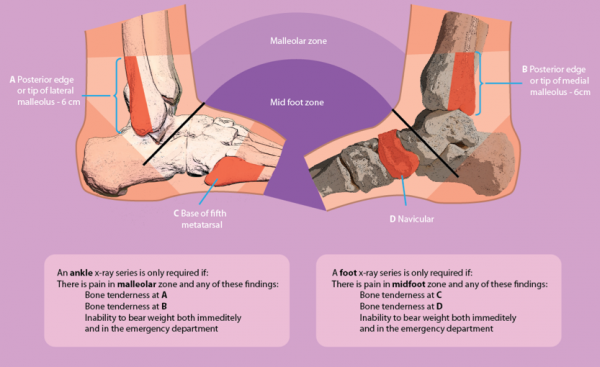
Ankle Sprain - Physiopedia
Acute ankle sprain in athletes: Clinical aspects and algorithmic
9 Best Sprained ankle exercises ideas ankle exercises, sprained ankle, sprained ankle exercises